The month of October makes most people think of pumpkin spice lattes, vibrant leaves, and Halloween costumes. But here at Premier Orthopaedics, we have something else we keep an eye out for, too, because it's also the time of year known as National Spine Health...
LATEST BLOGS
September is National Vascular Disease Awareness Month
As September starts, it's National Vascular Disease Awareness Month. This is a great time to learn about the health of our veins and arteries. Vascular diseases include problems like deep vein thrombosis and peripheral arterial disease. Read on to learn how to keep...
Causes & Treatment Options for Sciatica
Pain that starts in the lower back and radiates down the back of the leg is what is commonly referred to as sciatica. The pain follows the path of the sciatic nerve down the leg which means that typically, only one side of the body is affected. The sensation that...
Sports Medicine 101 for Athletes

Athletes are constantly pushing their bodies to meet the many demands involved with training for a sport and participating in games. While it’s important to stay in shape as an athlete, these intense activities can be damaging to the body.
Sports medicine is dedicated to treating the inevitable injuries that occur during exercise involving ligaments, tendons, muscles, and bones. The physicians in this field are licensed and trained in sports and exercise medicine to handle all types of sports injuries. There are also four different areas of focus these physicians can specialize in. These specialties include: orthopaedic surgery, sports rehabilitation, spine rehabilitation, and non-surgical treatments. Those involved in the field of sports medicine include medical physicians, physical therapists, athletic trainers, and massage therapists.
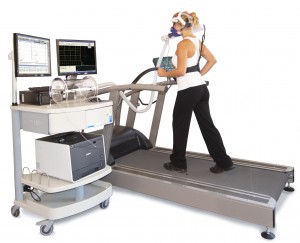
Exercise Physiologist
In addition to treating injuries, sports medicine specialists can help athletes get their bodies into great shape. These specialists evaluate the athlete’s overall health to get a better idea of their cardiovascular function, and design training programs based on those results. These programs will help athletes with their physical fitness, strength, endurance, flexibility, and overall performance. The specialists will help athletes understand the importance of listening to the body’s warning signs to determine what it needs. They are also skilled in assisting athletes with taking care of their bodies and helping them stay fit while also preventing muscle sprains, strains, and tears.
Nutrition
Diet and nutrition play an important role in allowing athletes to perform the best they can. A nutritionist can develop an individual diet plan based on what you’re looking to achieve, such as more energy and more nutrients to strengthen muscles and help them recover faster after a workout.
Physical Therapy
Sports medicine mainly focuses on treating injuries with non-surgical methods, such as physical therapy. This technique uses repetitive exercises to strengthen muscles, ligaments, and tendons after injury.
A physical therapist will evaluate the injury and determine the best course of action. He or she will develop a detailed, individualized program that involves stretching, exercise, and massage to aide in recovery.
Physical therapy sessions are conducted at a facility where you’ll be instructed and assisted with exercises. Sometimes, fitness equipment such as resistances bikes, treadmills, and whirlpools will be used. Your physical therapist will most likely have you performing some of these exercises at home, even after you’ve recovered, to increase flexibility and allow you to regain a full range of motion.
If you’re an athlete or exercise regularly, seeing a sports medicine professional can be beneficial for your health and your athletic performance. He or she will be able to treat your injury, teach you how to enhance your performance by eating better and listening to your body, and prevent injuries from occurring.
For more information about sports medicine, click here to download our e-book, The Athlete’s Guide to Reaching Peak Sports Performance and Preventing Injury. This educational guide will help you understand common sports injuries, treatment methods and how to maintain fitness after an injury.