Shoulder pain has a way of creeping into nearly every part of daily life. Simple movements — like reaching into a cabinet, fastening a seatbelt, getting dressed, or even finding a comfortable sleeping position — can suddenly become frustrating or downright painful....
Sleep plays a vital role in healing, recovery, and overall well-being. Unfortunately, hip pain can make getting a full night’s rest feel nearly impossible. Tossing and turning to find a comfortable position, waking up from sharp or aching pain, or starting the morning...
If you are struggling with lower back pain that radiates down your leg, you might have hit the internet searching for answers, only to find the terms “sciatica” and “herniated disc” discussed frequently. This is because both conditions can cause debilitating back...
Running Injuries that Require Physical Therapy

Running is an effective way to stay physically fit. It strengthens bones and knees, lowers risks of cancer and stroke, thwarts depression, improves lung function, burns calories and builds muscles. These benefits should be considered sufficient to include running in one’s daily routine. But before deciding to become an avid runner, it is essential to be informed that running can lead to certain injuries and most of these require physical therapy.
Causes of Running Injuries
While running is a good way to improve physical and mental health, it can cause injuries when performed incorrectly. Here are some common causes of running injuries:
- Running while wearing the wrong type and size of shoes
- Inadequate stretching
- Excessive running mileage in a short span of time
- Sudden modification in running pace
- Inadequate rest before running again
Running Injuries That Require Physical Therapy
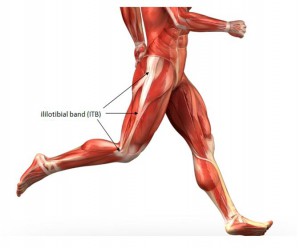
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)
This may develop due to too much friction on the iliotibial band – a dense mass of tissue that is located on the lateral part of the knee that goes up to the external part of the pelvis, above the hip and knee. It steadies the knee when you are running by moving behind and in front of the femur. Symptoms include thickening of the tissue and stinging sensations.
Piriformis Syndrome
Piriformis is a muscle in the gluteal region that stabilizes the hip. It can be irritated due to insufficient stretching and strength training. Symptoms include pain on the buttocks and hips.
Patellofemoral Stress Syndrome (PFSS)
This can develop due to tension in the iliotibial band, prolonged repetitive compressive forces and weakening of the hip and thigh muscles. Pain is usually felt on the back of the kneecap.
Shin Splints
This is also called Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS) and is characterized by pain on the inner edge of the tibia or anterior tibialis tendon. It can become inflamed due to excessive amounts of eccentric muscle activity and undertaking hard-impact physical activities on solid hard surfaces like running on asphalt.
Bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae or small sacs of synovial fluid in the body. It is characterized by redness, swelling and pain. Runners usually get hip or knee bursitis.
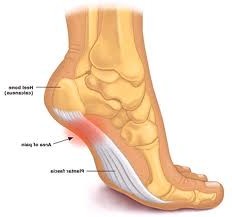
Plantar Fasciitis
It is also called “jogger’s heel” simply because it is common among joggers. Plantar Fasciitis refers to the inflammation and formation of excess fiber or structural weakening of the thick band of fascia at the bottom of the foot. Symptoms include sharp pain, numbness, tingling and swelling.
Blisters
These are fluid-filled sacs on the upper surfaces of the skin. Runners can get blisters due to excessive friction between the skin and shoes and socks.
When is Physical Therapy Needed?
The orthopaedic doctor will assess the injury thoroughly before prescribing the appropriate treatment. Physical therapy is usually recommended for mild cases but can also be used to complement other types of treatment. A licensed physician should be consulted to get the best results.
During physical therapy, expect the therapist to massage, mobilize and manipulate the affected area. You might be asked to perform certain type of exercises that improve balance and strength. Some of the tools that you will be using are:
- Resistance bands
- Foam rollers
- Steps of varying heights
- Pilates reformers and chairs
- Stability balls
If you feel any discomfort on your feet, knees, hips or any other part of the body that is involved in running, consult an orthopaedic doctor right away. It is important to address the problem immediately so you can enjoy more mileage.